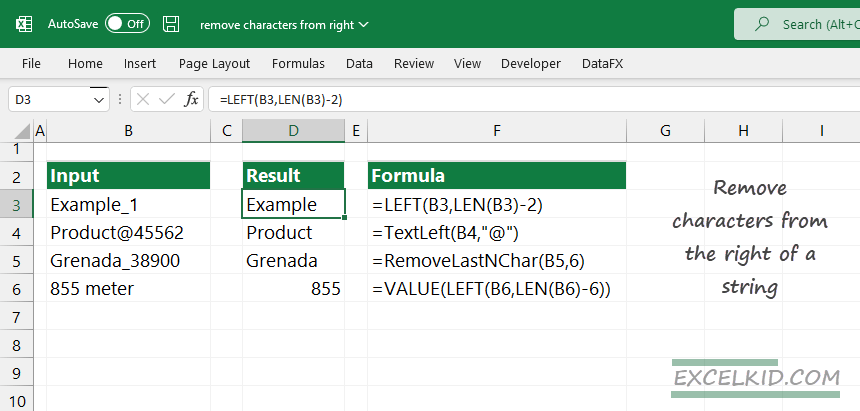
Learn how to remove characters from the right of the text using Excel functions. Discover how to remove the last n characters from a string.
You can save time using a versatile Excel toolbox with custom functions. This article will explain the most used formula examples and function syntaxes. If you want to dive deeply into Excel Formulas, read our definitive guide.
How to remove characters from the right?
Here are the steps to remove one or more characters from the right of a text string:
- Get the length of the text: =LEN(text)
- Remove n characters from the total length: =LEN(text)-n
- Extract the left part: =LEFT(text,LEN(text)-n)
Generic formula
=LEFT(text,LEN(text)-n)
LEFT function arguments:
- text: the text from which you want to remove the last n characters in Excel
- numbers_of_characters: the number of characters we want to remove
LEN function arguments:
- text: the cell that contains text
Let us examine the formula above! We have some functions to strip characters from the right. But we want to find a solution to make sure everyone clearly understands. So, we’ll apply an inverse formula and try to extract the characters from the left.
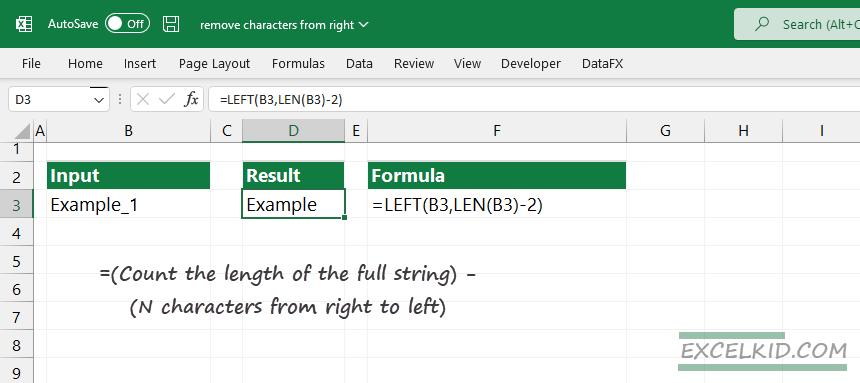
What should we do? Calculate the result using the following logic:
=(Count the length of the full string) – (N characters from right to left)
Explanation:
First, we extract the given number (n characters) from the left of the text.
=LEN(B3)-2) = 6
Now, we know the proper length of the string. It’s time to execute the second part of the formula. We will use the result as an argument for the LEFT formula. To remove the last n characters, combine the LEFT and LEN functions.
=LEFT(B3,6) = Example
TEXTLEFT function to remove characters from the right
The TEXTLEFT function did not exist in Excel by default. Fortunately, we have implemented a huge custom function library into our free Excel add-in. We’ll show you an example to demonstrate the power of user-defined functions.
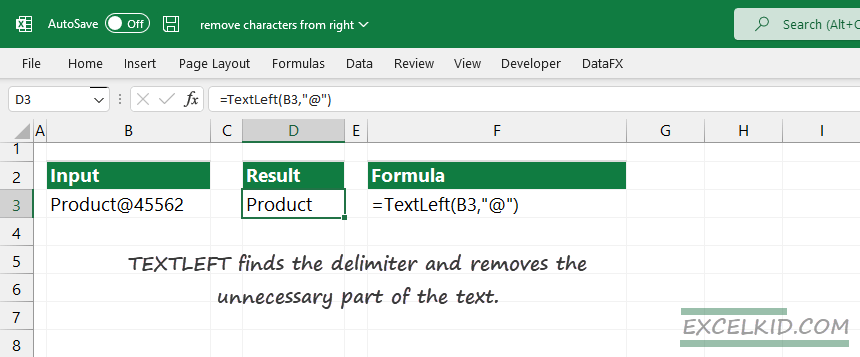
Enter the following formula in D3:
=TEXTLEFT(B3,”@”)
The function finds the delimiter and removes the unnecessary part of the text. TEXTLEFT is effective if you work with delimiters or wildcards in Excel.
Remove characters from the right using VALUE
Let’s look at the following example! We want to extract 855 from cell A5. LEN calculates the total length of the string in A6. The result is 9.
=LEFT(B3,LEN(B3)-6)
The formula returns” 855″; because it is a text value, we have to convert it to number format!
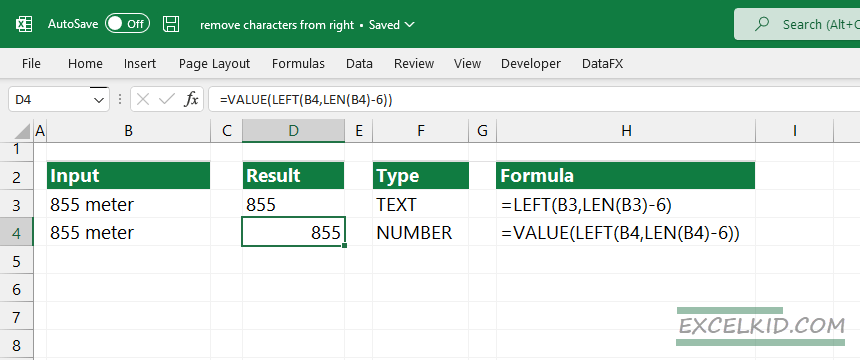
Apply the formula below that contains the VALUE function:
=VALUE(LEFT(B4,LEN(B4)-6))
Remove the last nth characters using VBA
If you have a data cleaning task, in some cases, we have to keep only the specific parts of a text or string.
Because we are familiar with VBA programming, we are working on our main goal: to write time-saving user-defined functions for the Excel community.
Take a closer look at the small code below:
Function RemoveLastNchar(rng As string, counter As Long)
RemoveLastNchar = LEFT(rng, LEN(rng) - counter)
End FunctionAs you see, the UDF combines the LEFT and LEN functions into a single function.
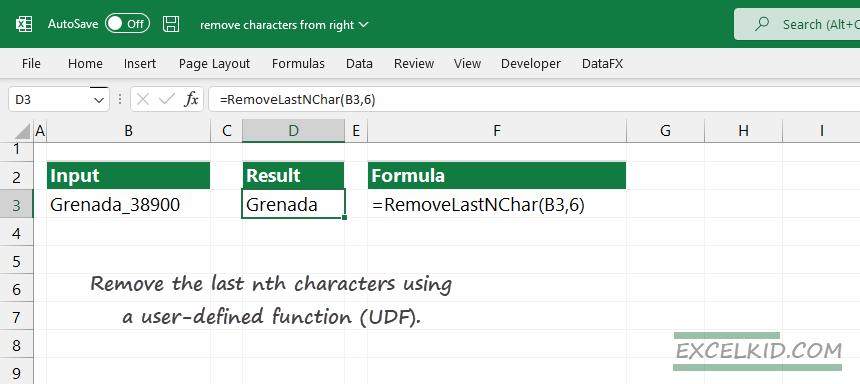
Delete the last n characters from the right using VBA
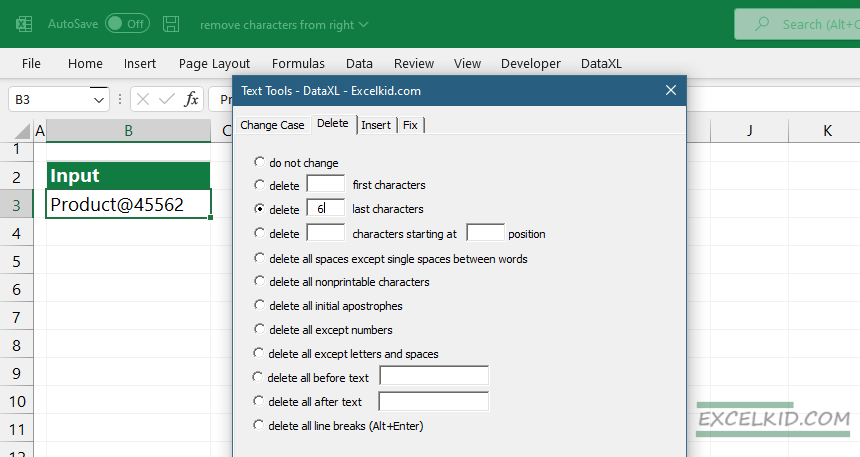
Use the DataXL Productivity Suite for Excel and follow the steps below:
- Locate the DataXL tab on the ribbon. Select the cell that contains the text.
- Click on the Text Tools icon. A new window will appear. Select the second tab, Delete.
- Enter the value.
- Example: To remove the last six characters from the right, use “6” as a parameter.
String Manipulation functions
- Using MID and SEARCH Functions: While the LEFT function is invaluable for extracting text from the beginning of a string, combining MID with SEARCH allows for more dynamic extractions, especially when dealing with variable-length strings or when the text to be removed isn’t always at the end.
- SUBSTITUTE and REPLACE Functions: These functions offer precision in text manipulation, allowing you to replace specific characters, words, or phrases within a string or to substitute the nth occurrence of a given character.
- TRIM and CLEAN Functions: Beyond removing characters, cleaning up text data often requires removing extra spaces (TRIM) and non-printable characters (CLEAN) to ensure consistency and accuracy in data analysis.