The Excel TRANSPOSE function swaps a vertical range to a horizontal range and switches rows to columns but keeps the data structure.
Table of contents:
- Convert rows to columns in Excel using Transpose
- Excel Transpose Shortcut
- How to use Excel Transpose Function
- Convert rows to Columns (VBA solution)
- Transpose Data using PowerQuery
- Excel Online (Web) Script
Steps to convert rows to columns using Transpose
- Copy the Data: Select the data range you want to transpose and press Ctrl + C to copy it.
- Choose the Paste Location: Click on the cell where you want the transposed data to start.
- Open Paste Options: Go to the Home tab, click on Paste, and choose Transpose.
Example
In this tutorial, you will use the Paste Special command menu to transpose data in Excel.
Our table contains sales data: products, period, and sales. First, select the range (rows and columns) that you want to transpose. Then, copy the data to the Clipboard using the Ctrl + C keyboard shortcut.
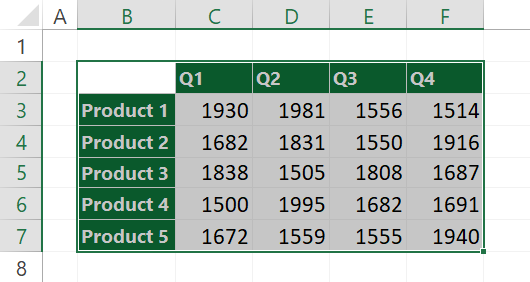
After that, select the Home Tab and click the Paste option. A drop-down list containing some paste options will appear.
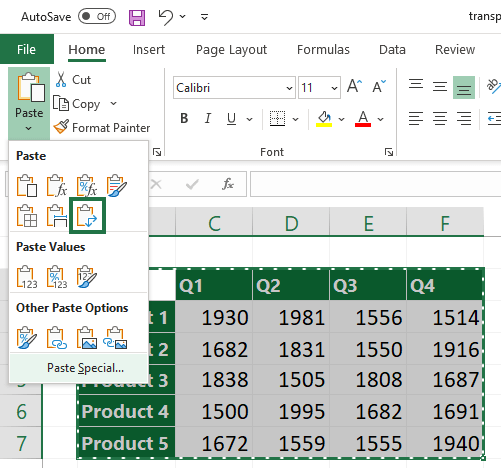
Select the target cell where you want to place the transposed data. The selected cell will be the top-left corner of the transposed data. Click on the Transpose icon to paste the data.
How to use the Transpose Excel Shortcut
Steps to transpose data using shortcuts:
- Select the source range, then use the Ctrl + C shortcut
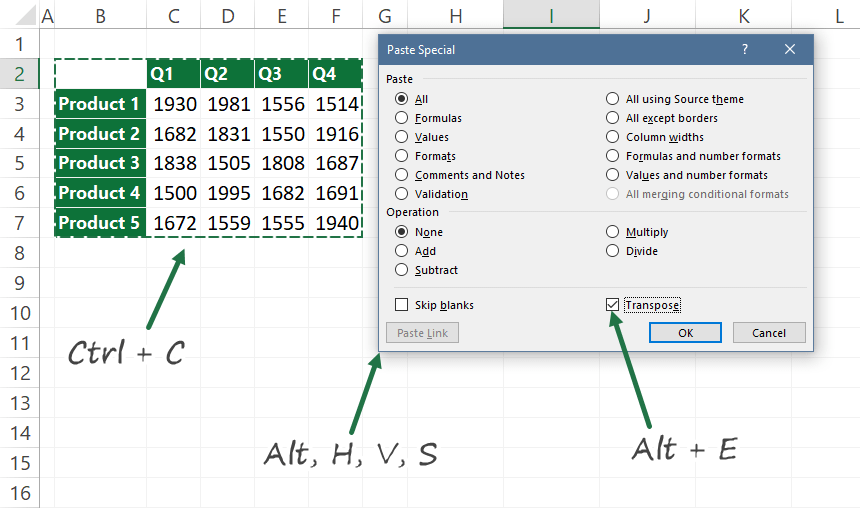
- Select the target range, then apply the Alt, H, V, S shortcut to open the Paste Special dialog box
- Check the Transpose option manually, or use the Alt + E shortcut to select the Transpose checkbox.
- Press OK to paste the data.
The shortcut helps rearrange data without quickly copying and pasting individual cells.
How to use Excel Transpose Function
The Excel TRANSPOSE function converts a vertical range of cells to a horizontal range of cells. It’s a reverse function, and you can convert a horizontal range of cells to a vertical range of cells.
In other words, the function replaces the orientation of a given range or array:
- If you have a vertical range, TRANSPOSE converts it to a horizontal range
- In the case of horizontal range, TRANSPOSE converts it to a vertical range
It’s good to know that the transposed range is dynamic. What does this mean in practice? If you change one or more values in the source range, the Excel Transpose function will update the target range data.
Steps to convert rows to columns using Array Formula
Use this method if you are working with Excel 2013, Excel 2016, or Excel 2019.
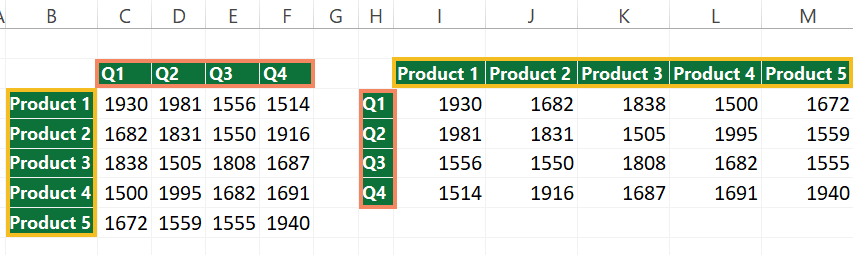
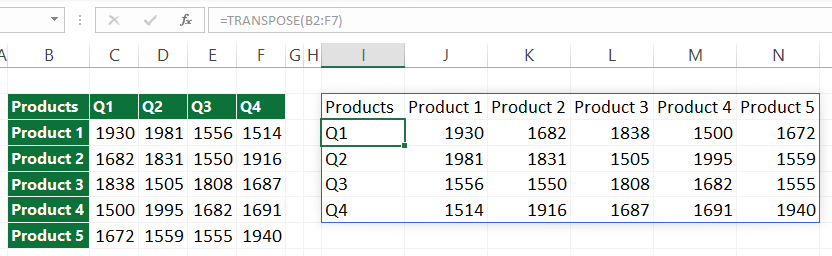
In the first example, take a closer look at the range B2:F7! The range, in this case, is a 6×5 matrix. You want to change the orientation and convert the selected cells into a horizontal array. So, you must choose a target range containing five rows and six columns.
Select the target range; in this case H2:M6
Go to Formula Bar and enter the formula. Use the =TRANSPOSE(B2:F7) formula, but don’t hit Enter. Instead, create an array formula using the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys.
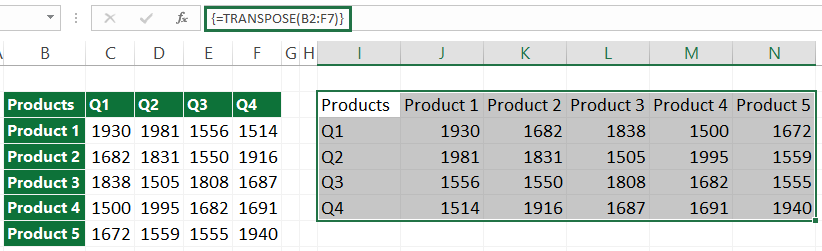
After pressing the Ctrl + Shift + Enter, you will get the result quickly. When you see curly brackets around the formula, the transformation was successful. These curly brackets are how Excel recognizes an array formula.
Transpose data in Excel using Microsoft 365
We strongly recommend you use the latest Excel; now, you will learn why. In addition, the simplified Transpose Excel function provides time-saving tricks.
Differences between old and spilled array formulas in Excel: Legacy array formulas (you can find them in older Excel versions) always return a fixed-size result. However, when you press Enter to confirm the Transpose formula in the latest version of Microsoft Excel, Excel will dynamically size the output range and place the results into each cell within that range.
Let us see how the spill feature works:
Select cell I2, then enter the range that you want to transpose.
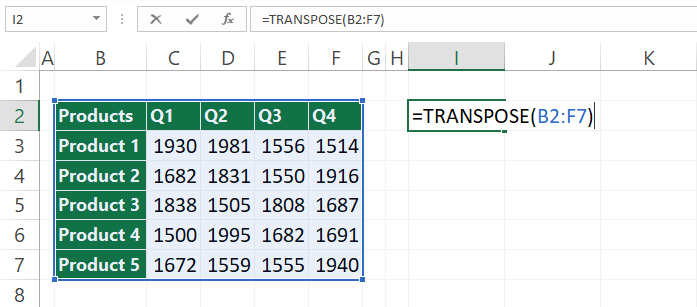
Press Enter! If you are working with the latest Excel, using the curly bracket and the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keystroke is unnecessary.
Once you enter a spilled array formula, Excel will place a highlighted border around the transposed range when selecting any cell within the spill area. The blue border will disappear when you select any cell outside the transposed range.
What a great feature: paste a range into a single cell. Don’t forget: Excel still supports the old Ctrl + Shift + Enter method for backward compatibility reasons.
Convert rows to Columns using VBA
If you are familiar with Visual Basic for Applications, you can write macros. Then, run the macro from the Developer Tab or place it in the Quick Access Toolbar.
Use the Alt + F11 shortcut to open the VBA editor window. Then, copy the code below into a new module.
Sub QuickTranspose()
Dim vFormulas As Variant
Dim oSel As Range
Set oSel = Selection
vFormulas = oSel.Formula
vFormulas = Application.WorksheetFunction.Transpose(vFormulas)
oSel.Offset(oSel.Rows.Count + 2).Resize(oSel.Columns.Count, oSel.Rows.Count).Formula = vFormulas
End SubAdd the macro to the QAT if you use the Transpose function frequently.
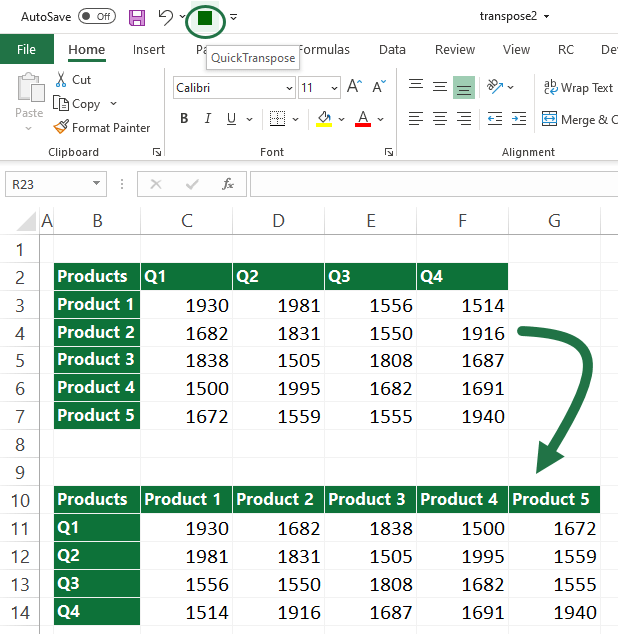
You can use the Alt, 4 shortcut to transform your data in the example.
Transpose Data using PowerQuery
Follow this guide when you store data in an Excel Table and need to use the transpose function frequently.
First, select the range you want to transpose. Then, locate the Data tab on the ribbon and use the From Table/Range function.
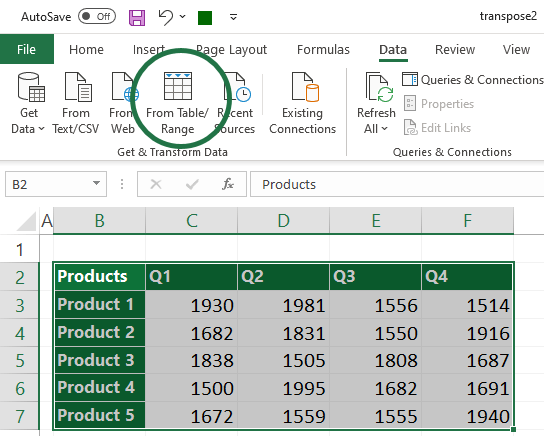
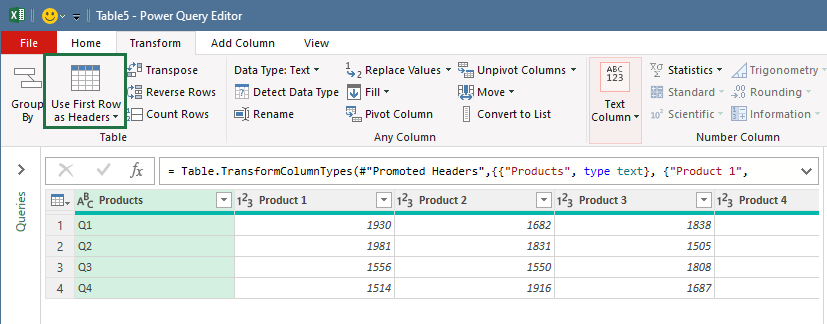
The Power Query editor window will appear. Select the Transform tab, and click ‘Use Headers as First Row’ from the ‘Use First Row as Headers’ drop-down list.
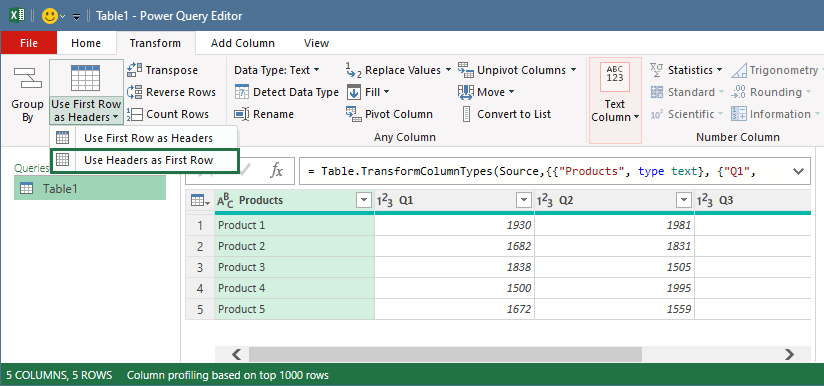
Select the Transform tab in the Power Query Editor and convert rows to columns using the Transpose command.
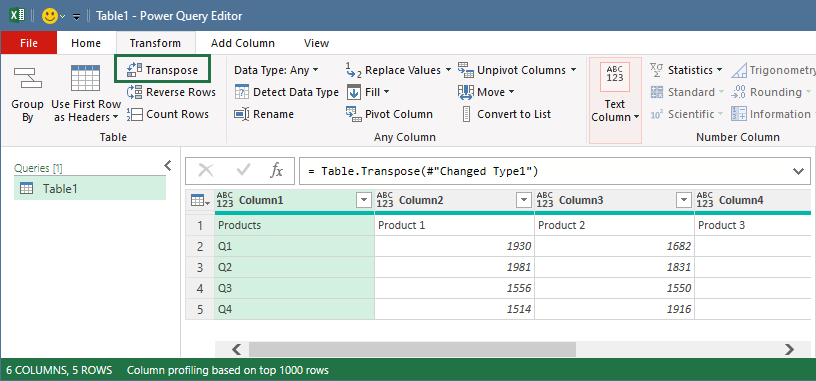
Once Excel transposes the data, you need to switch the column header back. To do that, select the Use First Row as Headers to promote the first row of this table into column headers.
Now, you want to get back to Excel and check your data. But first, go to the Home tab and click the Close and Load button.
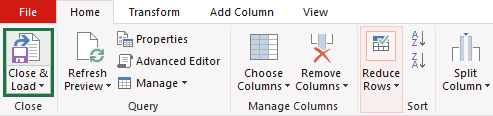
Excel will place the transposed data into a new Worksheet.
Excel Online (Web) Transpose Script
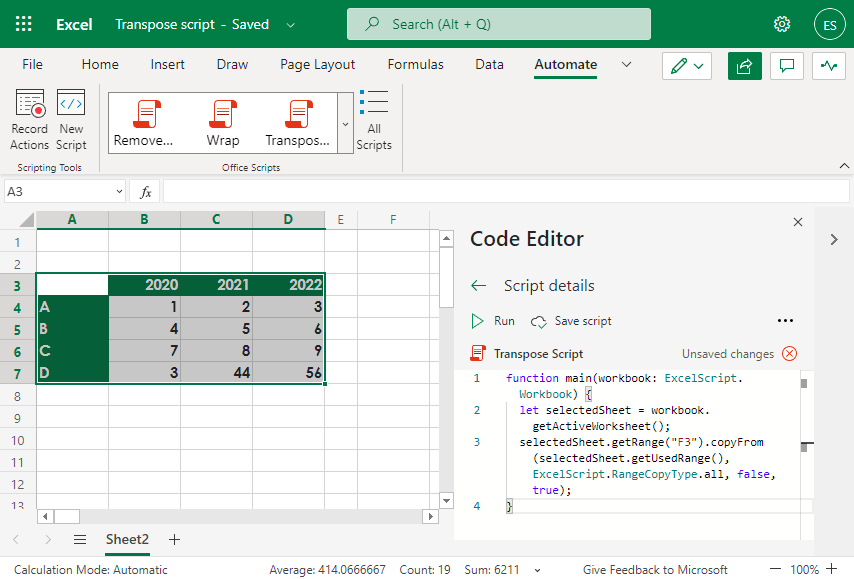
If you are working with the web version of Microsoft Excel, you can use the typescript language to create simple and complex scripts.
Locate the Automate tab on the ribbon and click on New Script to reach the Code Editor on the right pane.
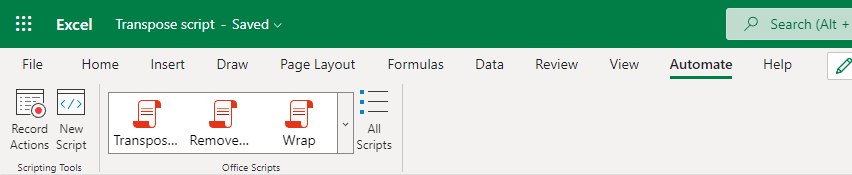
Insert the following script. The script will transpose the selected range and then paste the data to the range started with cell F3.
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
let selectedSheet = workbook.getActiveWorksheet();
selectedSheet.getRange("F3").copyFrom(selectedSheet.getUsedRange(), ExcelScript.RangeCopyType.all, false, true);
}Finally, add a new name, then save the script. Run the script and convert rows to columns quickly! The script will place the converted range, starting with cell F3. You can easily change this parameter to place the get result in another sheet or range.
Wrapping things up
- Use dynamic arrays if you are working with the latest Excel, Microsoft 365
- Remove filters before applying Transpose
- Use the Quick Access Toolbar to speed up your work
- If it is possible, use shortcuts
- If you have large data tables, use Power Query